# Introduction
To run a Kubernetes into local machine you have several options.
Minikubeis a virtual machine based solution.Microk8sis a snap package, available only in Ubuntu and compatible distributionsDocker Desktopis an application for MacOS and Windows machines
I this article we explore another option, k3d (opens new window) a docker version of k3s, the lightweight Kubernetes distribution by Rancher.
# What is k3s (the official definition)
k3s is a fully compliant Kubernetes distribution with the following changes:
- Packaged as a single binary.
- Lightweight storage backend based on sqlite3 as the default storage mechanism. etcd3, MySQL, Postgres also still available.
- Wrapped in simple launcher that handles a lot of the complexity of TLS and options.
- Secure by default with reasonable defaults for lightweight environments.
- Minimal to no OS dependencies (just a sane kernel and cgroup mounts needed). k3s packages required
dependencies
- containerd
- Flannel
- CoreDNS
- CNI
- Host utilities (iptables, socat, etc)
- Ingress controller (traefik)
- Embedded service loadbalancer
- Embedded network policy controller
# What is k3d
k3d is a Go binary file that run k3s in docker. A very simple installation way and no modification in your system just one docker container that contain the Kubernetes cluster.
# Requirements
- docker
- kubectl
- java
- helm (opens new window)
# Install k3d
The installation script install.sh will run the following steps
initArch # discovers the architecture for this system
initOS # discovers the operating system for this system
verifySupported # checks that the os/arch combination is supported for binary builds
checkTagProvided || checkLatestVersion
if ! checkK3dInstalledVersion; then
downloadFile # downloads the latest binary package and also the checksum
installFile # make the Go binary file executable and mv it to /usr/local/bin/.
fi
:${K3D_INSTALL_DIR:="/usr/local/bin"}
...
installFile() {
echo "Preparing to install $APP_NAME into ${K3D_INSTALL_DIR}"
runAsRoot chmod +x "$K3D_TMP_FILE"
runAsRoot cp "$K3D_TMP_FILE" "$K3D_INSTALL_DIR/$APP_NAME"
echo "$APP_NAME installed into $K3D_INSTALL_DIR/$APP_NAME"
}
To install k3d run the following command
$ curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rancher/k3d/v1.7.0/install.sh | bash
# Create a cluster
To create a Kubernetes cluster run the following command
$ k3d create
INFO[0000] Created cluster network with ID aa64941776d3cfd783189cbb46c0abbee89074228d3f88d7748d17f28cc9f0ca
INFO[0000] Created docker volume k3d-k3s-default-images
INFO[0000] Creating cluster [k3s-default]
INFO[0000] Creating server using docker.io/rancher/k3s:v1.17.3-k3s1...
INFO[0000] Pulling image docker.io/rancher/k3s:v1.17.3-k3s1...
INFO[0006] SUCCESS: created cluster [k3s-default]
INFO[0006] You can now use the cluster with:
export KUBECONFIG="$(k3d get-kubeconfig --name='k3s-default')"
kubectl cluster-info
If you run the following command you can see that there are a k3s docker image just pulled.
$ docker ps | grep k3s
b0c341cbee7a rancher/k3s:v1.17.3-k3s1 "/bin/k3s server --h…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:6443->6443/tcp k3d-k3s-default-server
If you run the following command you can see that there are a k3d-k3s... container running.
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
b0c341cbee7a rancher/k3s:v1.17.3-k3s1 "/bin/k3s server --h…" 2 minutes ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:6443->6443/tcp k3d-k3s-default-server
# Generate kubectl configuration
To user the Kubernetes cluster we need to tell kubectl where to find the config file.
k3d a command to get the config file location
$ k3d get-kubeconfig --name='k3s-default'
/home/..../.config/k3d/k3s-default/kubeconfig.yaml
We set this path into KUBECONFIG kubectl environment variable
$ export KUBECONFIG="$(k3d get-kubeconfig --name='k3s-default')"
# Check that the cluster is running
$ kubectl get pod,svc --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system pod/local-path-provisioner-58fb86bdfd-qrmmv 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system pod/metrics-server-6d684c7b5-qk4pl 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system pod/helm-install-traefik-qb7mn 0/1 Completed 0 23m
kube-system pod/svclb-traefik-748m5 2/2 Running 0 23m
kube-system pod/coredns-d798c9dd-tth8c 1/1 Running 0 23m
kube-system pod/traefik-6787cddb4b-qswjk 1/1 Running 0 23m
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.43.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23m
kube-system service/kube-dns ClusterIP 10.43.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 23m
kube-system service/metrics-server ClusterIP 10.43.94.13 <none> 443/TCP 23m
kube-system service/traefik-prometheus ClusterIP 10.43.110.75 <none> 9100/TCP 23m
kube-system service/traefik LoadBalancer 10.43.54.34 172.19.0.2 80:32219/TCP,443:32350/TCP 23m
# Build and deploy demo application
# Create a demo application
Create an new spring-boot application using https://start.spring.io/. For this tuto we will use an already prepared application from demo-app-istio-k3d (opens new window) repository.
$ git clone https://github.com/mohamedelhabib/demo-app-istio-k3d
# checkout the 1.0 tag
$ git checkout 1.0
At this step we have a very simple spring-boot application with
spring-boot-starter-webto run a tomcat serverspring-boot-starter-actuatorto get /actuator/info endpoint
We are using the jib-maven-plugin to generate the docker image. Please see the pom.xml for more details.
$ tree .
.
├── HELP.md
├── k8s
│ ├── 01_namespace.yml
│ ├── 02_deployment.yml
│ └── 03_service.yml
├── mvnw
├── mvnw.cmd
├── pom.xml
└── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── example
│ │ └── demoistio
│ │ └── DemoIstioApplication.java
│ └── resources
│ └── application.properties
└── test
└── java
└── com
└── example
└── demoistio
└── DemoIstioApplicationTests.java
# Build the demo application
To build the application jar and docker image run the following command
$ ./mvnw clean package
You can check that there are a docker image com.example/demo-app
$ docker image ls | grep demo
com.example/demo-app 1.0 486ace0e9548 50 years ago 383MB
To deploy our application into the Kubernetes cluster we have to make our local image available into the cluster. This can be done by push the image to a remote docker registry or by using the import-images
$ k3d import-images com.example/demo-app:1.0
INFO[0000] Saving images [com.example/demo-app:1.0] from local docker daemon...
INFO[0000] Pulling image docker.io/iwilltry42/k3d-tools:v0.0.1...
INFO[0006] Saved images to shared docker volume
INFO[0006] Importing images [com.example/demo-app:1.0] in container [k3d-k3s-default-server]
INFO[0011] Successfully imported images [com.example/demo-app:1.0] in all nodes of cluster [k3s-default]
INFO[0011] Cleaning up tarball
INFO[0011] Deleted tarball
INFO[0011] ...Done
# Deploy the demo application
Into k8s folder you can the k8s manifest we will use to deploy.
The demo-app will be deployed into namespace api
$ tree k8s/
k8s/
# manifest to create the `api` namespace
├── 01_namespace.yml
# manifest to create deploy container using the demo-app docker image
├── 02_deployment.yml
# manifest to create a Kubernetes service
└── 03_service.yml
Fill free to check the content of YAML file
Run the following command to deploy and wait to deployment to finish.
Wait until you see 1/1 into READY columns, Tape CTRL+C to stop waiting.
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s && kubectl -n api get pods -w
namespace/api created
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment created
service/demo-app-service created
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
demo-app-deployment-f444966fd-4qh5n 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 0s
demo-app-deployment-f444966fd-4qh5n 0/1 Running 0 2s
demo-app-deployment-f444966fd-4qh5n 1/1 Running 0 5s
To check pod is running and service is there run the following command
$ kubectl -n api get pods,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/demo-app-deployment-f444966fd-l6hn9 1/1 Running 0 6m52s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/demo-app-service ClusterIP 10.43.10.248 <none> 80/TCP 6m52s
To check that application is running, we connect to the server docker container and run a simple http request.
NOTE that 10.43.10.248 is the IP show into CLUSTER-IP into previous command
$ docker exec -ti k3d-k3s-default-server sh -c "wget -qSO- 10.43.10.248/actuator/info"
HTTP/1.1 200
Content-Type: application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v3+json
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Date: Fri, 15 May 2020 04:13:56 GMT
Connection: close
{"git":{"branch":"67f84b9744d014f558b95fb521266fa4fb00501a","commit":{"id":"67f84b9","time":"2019-12-05T12:04:13Z"}}}
# Deploy Istio into k3d
# What is Istio
Istio provides behavioural insights and operational control over the service mesh as a whole, offering a complete solution to satisfy the diverse requirements of microservice applications. Read more about provided features here https://istio.io/docs/concepts/what-is-istio/
# Disable k3s load balancer service
k3s and k3d come with preconfigured load balancer service, this is fine for default usage, but to be able de use istio we have to disable this service.
Unfortunately k3s don't provide an update cluster option, so we have to recreate the cluster. More details into this github issue https://github.com/rancher/k3d/issues/104
Hopefully this very easy and quick to do.
Run this command to delete the cluster.
$ k3d delete
INFO[0000] Removing cluster [k3s-default]
INFO[0000] ...Removing server
INFO[0002] ...Removing docker image volume
INFO[0002] Removed cluster [k3s-default]
Run this command to create the cluster without the load balancer service.
$ k3d create --server-arg --no-deploy --server-arg servicelb
Run the following commands to deploy the application
$ k3d import-images com.example/demo-app:1.0
$ export KUBECONFIG="$(k3d get-kubeconfig --name='k3s-default')"
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s && kubectl -n api get pods -w
# Download and extract Istio
$ curl https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.5.4/istio-1.5.4-linux.tar.gz -L | tar xvz
# Create a namespace for istio
$ cd istio-1.5.4
$ kubectl create namespace istio-system
namespace/istio-system created
# Install istio-init
$ helm template istio-init install/kubernetes/helm/istio-init --namespace istio-system | kubectl apply -f -
serviceaccount/istio-init-service-account created
configmap/istio-crd-all created
configmap/istio-crd-mixer created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/istio-init-istio-system created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/istio-init-admin-role-binding-istio-system created
job.batch/istio-init-crd-all-1.5.4 created
job.batch/istio-init-crd-mixer-1.5.4 created
# Wait that `istio-init-crd` are `Completed`
$ kubectl get pod,svc -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/istio-init-crd-mixer-1.5.4-6hjst 0/1 Completed 0 50s
pod/istio-init-crd-all-1.5.4-qlfdp 0/1 Completed 0 50s
# Install Istio
At this step we will install Istio with Kiali (an observability console for Istio).
To activate this console we need to provide a login/password
Using kubectl we create a Keberntes Secret containing the username and passphrase for Kiali
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: kiali
namespace: istio-system
labels:
app: kiali
type: Opaque
data:
username: YWRtaW4=
passphrase: YWRtaW4=
EOF
Using helm we deploy the chart of Istio
$ helm template istio install/kubernetes/helm/istio --namespace istio-system --set kiali.enabled=true | kubectl apply -f -
oddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-galley created
poddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-ingressgateway created
poddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-policy created
poddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-telemetry created
poddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-pilot created
poddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-citadel created
poddisruptionbudget.policy/istio-sidecar-injector created
...
...
rule.config.istio.io/promhttp created
rule.config.istio.io/promtcp created
rule.config.istio.io/promtcpconnectionopen created
rule.config.istio.io/promtcpconnectionclosed created
rule.config.istio.io/kubeattrgenrulerule created
rule.config.istio.io/tcpkubeattrgenrulerule created
job.batch/istio-security-post-install-1.5.4 created
check that every thing is OK (status should be Completed or Running)
$ kubectl get pod,svc -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/istio-init-crd-mixer-1.5.4-t5mjk 0/1 Completed 0 111s
pod/istio-init-crd-all-1.5.4-7phvs 0/1 Completed 0 111s
pod/istio-citadel-5449c98845-cf7bb 1/1 Running 0 55s
pod/svclb-istio-ingressgateway-czd64 9/9 Running 0 55s
pod/istio-telemetry-85c9dfddb7-nx42k 2/2 Running 1 55s
pod/istio-policy-5db987b9dc-mmzgk 2/2 Running 1 55s
pod/istio-galley-554d6d4cfb-sjq87 1/1 Running 0 55s
pod/kiali-9fc79f8b8-rxc7n 1/1 Running 0 55s
pod/istio-sidecar-injector-85b6d84b84-72cfj 1/1 Running 0 54s
pod/prometheus-794594dc97-s5p2g 1/1 Running 0 55s
pod/istio-security-post-install-1.5.4-krv64 0/1 Completed 0 35s
pod/istio-pilot-786558d87b-hrs9f 2/2 Running 2 55s
pod/istio-ingressgateway-644cd99cfd-xsl6m 1/1 Running 0 55s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/istio-galley ClusterIP 10.43.62.172 <none> 443/TCP,15014/TCP,9901/TCP 55s
service/kiali ClusterIP 10.43.55.178 <none> 20001/TCP 55s
service/istio-policy ClusterIP 10.43.81.255 <none> 9091/TCP,15004/TCP,15014/TCP 55s
service/istio-telemetry ClusterIP 10.43.48.138 <none> 9091/TCP,15004/TCP,15014/TCP,42422/TCP 55s
service/istio-pilot ClusterIP 10.43.33.93 <none> 15010/TCP,15011/TCP,8080/TCP,15014/TCP 55s
service/prometheus ClusterIP 10.43.82.109 <none> 9090/TCP 55s
service/istio-citadel ClusterIP 10.43.177.192 <none> 8060/TCP,15014/TCP 55s
service/istio-sidecar-injector ClusterIP 10.43.31.119 <none> 443/TCP,15014/TCP 55s
service/istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.43.105.148 172.21.0.2 15020:30892/TCP,80:31380/TCP,443:31390/TCP,31400:31400/TCP,15029:31994/TCP,15030:32199/TCP,15031:30538/TCP,15032:30545/TCP,15443:30726/TCP 55s
# Test with istio demo application
$ kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
$ kubectl get pods -w
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
$ kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'
Goto this url to check istio demo working http://{The IP Address}/productpage Refersh several time and you should see three version of the review star
- black
- orange
- and none In fact the istio bookinfo application contains three versions of the review service
# Acces Kiali dashboard
Run this command to access the Kiali dashboard. it will create a port forward and open the right url into navigator.
$ ./bin/istioctl dashboard kiali
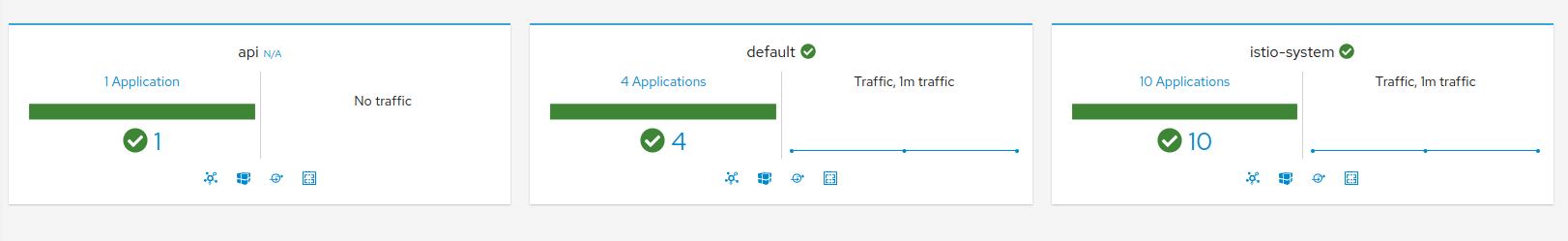
You should see some thing like this.
- 1 application into
apinamespace, ower demo application - 4 application into
default, the istio demo application - 10 application into
istio-system, the istio container
# Use Isto for the demo application
# Enable istio-injection into demo-app
Into this version 1.0-istio-injectio-on we enable the istio-injection by added a label into namespace api
$ git checkout 1.0-istio-injectio-on
$ git diff 1.0..1.0-istio-injectio-on
diff --git a/k8s/01_namespace.yml b/k8s/01_namespace.yml
index b61d02d..6bd1bae 100644
--- a/k8s/01_namespace.yml
+++ b/k8s/01_namespace.yml
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
- # labels:
- # # enable istio injection into the new namespace
- # istio-injection: enabled
- name: api
\ No newline at end of file
+ labels:
+ # enable istio injection into the new namespace
+ istio-injection: enabled
+ name: api
When we apply this modification, we can see that only namespace change pod is not updated.
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s && kubectl -n api get pods
namespace/api configured
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment unchanged
service/demo-app-service unchanged
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
demo-app-deployment-f444966fd-4qh5n 1/1 Running 0 61m
We need to restart pods to make the change applied. There are no restart command provided by kubectl. To achieve that we patch the deployment by adding a label this will make k8s create a new revision with the same image version
$ kubectl patch -n api deployment demo-app-deployment -p "{\"spec\":{\"template\":{\"metadata\":{\"annotations\":{\"restart_date\":\"$(date +'%s')\"}}}}}"
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment patched
$ kubectl -n api get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
demo-app-deployment-577f556689-tlpnn 2/2 Running 0 18s
You can see that the pod name has changed and under READY we have 2/2 instead of 1/1.
We can see that there are a new container called istio-proxy
$ kubectl -n api get pods demo-app-deployment-577f556689-tlpnn -o json | jq -r .spec.containers[].name
demo-app
istio-proxy
# Configuring ingress using an Istio gateway
To expose the demo-app outside the k8s cluster we need an Istio Gateway and an Istio VirtualService. An ingress Gateway describes a load balancer operating at the edge of the mesh that receives incoming HTTP/TCP connections. It configures exposed ports, protocols, etc. but, unlike Kubernetes Ingress Resources, does not include any traffic routing configuration. Traffic routing for ingress traffic is instead configured using Istio routing rules, exactly in the same way as for internal service requests.
$ git checkout 1.0-istio-gateway-as-ingress
This version add a new file k8s/04_gateway.yml, that contains the definition of the demo-app-gateway and the demo-app-route. We only expose the /actuator/* endpoints.
# Apply changes
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s
namespace/api unchanged
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment unchanged
service/demo-app-service unchanged
gateway.networking.istio.io/demo-app-gateway created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/demo-app-route created
# check that gateway is there
$ kubectl get gateway -n api
NAME AGE
demo-app-gateway 77s
# check that virtualservice is there
$ kubectl get virtualservices.networking.istio.io -n api
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
demo-app-route [demo-app-gateway] [*] 89s
# get the external IP of the istio-ingressgateway
$ kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'
172.24.0.2
# check that demo-app is accessible from outsie the k8s cluster
$ curl -v -s 172.24.0.2/actuator/info
* Trying 172.24.0.2:80...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 172.24.0.2 (172.24.0.2) port 80 (#0)
> GET /actuator/info HTTP/1.1
> Host: 172.24.0.2
> User-Agent: curl/7.65.3
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< content-type: application/vnd.spring-boot.actuator.v3+json
< date: Thu, 05 Dec 2019 16:02:39 GMT
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 3
< server: istio-envoy
< transfer-encoding: chunked
<
* Connection #0 to host 172.24.0.2 left intact
{"git":{"branch":"67f84b9744d014f558b95fb521266fa4fb00501a","commit":{"id":"67f84b9","time":"2019-12-05T12:04:13Z"}}}
# Api versionning
# Version 1
git checkout 1.1
This version contains a new Rest endpoint that generate a random name.
# build the version 1.1 of the docker image
$ ./mvnw clean package
$ docker image ls | grep demo
com.example/demo-app 1.0 486ace0e9548 50 years ago 383MB
com.example/demo-app 1.1 05a5c689c1b7 50 years ago 385MB
the deployment.yml reference now the 1.1 version of the image. We need to import this new version into k3s cluster. We have to update the
virtualserviceto be able to reach the new '/v1/hello' endpoint
$ k3d import-images com.example/demo-app:1.1
# Deploy version 1.1
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s
namespace/api unchanged
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment configured
service/demo-app-service unchanged
gateway.networking.istio.io/demo-app-gateway unchanged
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/demo-app-route configured
$ curl -v -s 172.24.0.2/v1/hello
* Trying 172.24.0.2:80...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 172.24.0.2 (172.24.0.2) port 80 (#0)
> GET /v1/hello HTTP/1.1
> Host: 172.24.0.2
> User-Agent: curl/7.65.3
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< content-type: text/plain;charset=UTF-8
< content-length: 18
< date: Thu, 05 Dec 2019 17:52:10 GMT
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 5
< server: istio-envoy
<
* Connection #0 to host 172.24.0.2 left intact
Hello, Mel Maggio!
# Version 1 and Version 2 canary release
When migrating from version 1 to version 2 of an API, We need to give time to client of this API to migrate, So we need to have the two version of API running together. To do that we will have to deployment, one for each version.
# Get version 1.2 code
git checkout 1.2
Note the
versionlabel: this is very important for Istio to distinguish between the two deployments
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: demo-app-deployment-v1
spec:
...
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: demo-app
version: v1.1
spec:
containers:
- name: demo-app
image: com.example/demo-app:1.1
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: demo-app-deployment-v2
spec:
...
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: demo-app
version: v1.2
spec:
containers:
- name: demo-app
image: com.example/demo-app:1.2
No big change to do into the kubernetes service
Note that the port is named (“name: http”). This is a requirement for Istio.
The selector is only using the
demo-applabel. Without Istio it will distribute traffic between the two deployments evenly.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
namespace: api
name: demo-app-service
labels:
app: demo-app
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
targetPort: 8080
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: demo-app
For VirtualService side, we use the subset. A subset/version of a route destination is identified with a reference to a named service subset which must be declared in a corresponding DestinationRule.
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /v1
route:
- destination:
host: demo-app-service
subset: v1
port:
number: 80
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /v2
route:
- destination:
host: demo-app-service
subset: v2
port:
number: 80
And here the definition of DestinationRule that make the mapping between Sebset/version and pods/version
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: demo-app-rules
namespace: api
spec:
host: demo-app-service
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
# Build the version 1.2 of the docker image
$ ./mvnw clean package
$ k3d import-images com.example/demo-app:1.2
# Deploy version 1.2 and 1.1
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s
namespace/api unchanged
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment-v1 created
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment-v2 created
service/demo-app-service configured
gateway.networking.istio.io/demo-app-gateway unchanged
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/demo-app-route configured
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/demo-app-rules created
$ kubectl apply -R -f k8s && kubectl -n api get pods
namespace/api unchanged
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment-v1 unchanged
deployment.apps/demo-app-deployment-v2 unchanged
service/demo-app-service unchanged
gateway.networking.istio.io/demo-app-gateway unchanged
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/demo-app-route unchanged
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/demo-app-rules unchanged
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
demo-app-deployment-c644498c8-6gln5 2/2 Running 0 27m
demo-app-deployment-v1-5fb699f946-j5vrg 2/2 Running 0 94s
demo-app-deployment-v2-5b7dd595fb-45lzp 2/2 Running 0 94s